Reconstructive Surgery For Cleft Lip-Palate
Reconstructive Surgery For Cleft Lip-Palate
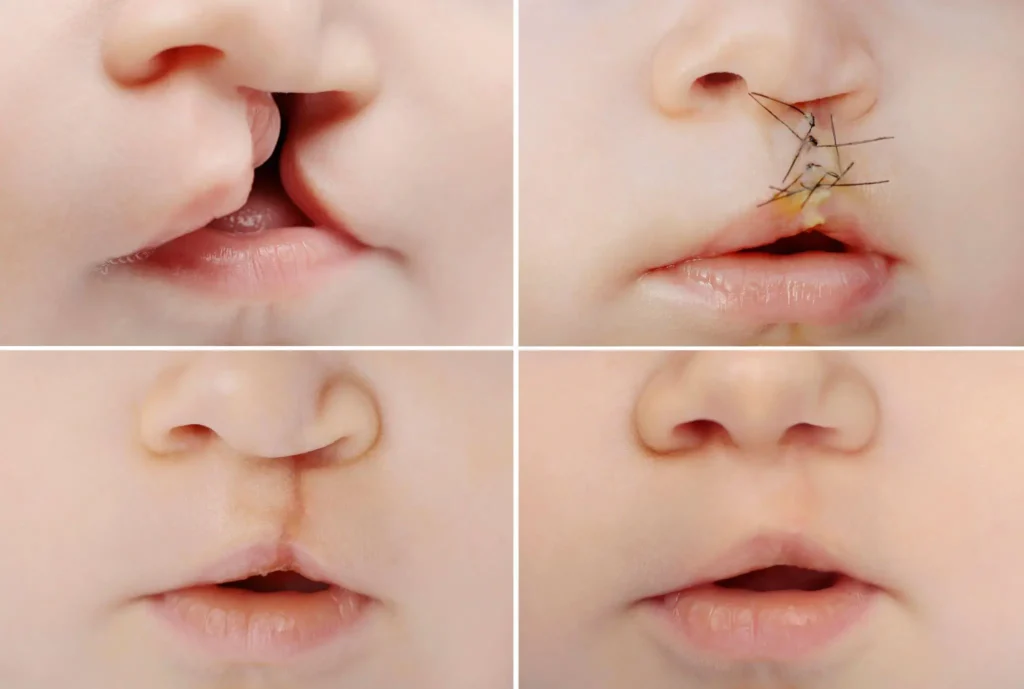
Cleft lip and cleft palate are two disorders that can occur individually or simultaneously. Lip cleft correction entails closing the cleft and is commonly done on babies at the age of three months. Cleft lip and palate repair is commonly done at 9 to 12 months of age.
What Is Cleft Lip And Palate
Cleft lip and palate are congenital defects that affect the face. The top lip has a gap or discontinuity known as a cleft lip. A cleft palate is a separation of the mouth and the nose in the roof of the mouth. Clefts occur when the lip and/or palate do not fully form during the first few weeks of pregnancy. During this phase, the face begins to take shape. To develop the lip and palate, separate plates of bone and tissue progressively migrate towards each other and unite. A cleft is formed when these components do not unite fully.
The most frequent facial deformities are cleft lip and palate. A cleft lip or palate affects around one out of every 700 live births. According to the World Health Organization: WHO, this accounts for roughly half of all craniofacial malformations. The likelihood of having a cleft lip and palate is determined by ancestry.
- Classification of Cleft Lip & Palate
- Causes of Cleft Lip & Palate
- Treatment Timeline of Cleft Lip & Palate
Complete cleft lip, unilateral cleft lip, and bilateral cleft lip are the three types of cleft lip.
- The term “incomplete cleft lip” refers to a gap in the top lip that does not involve the nose.
- The term “unilateral cleft lip” refers to a gap in the top lip that extends into the nose.
- The term “bilateral cleft lip” refers to two gaps in the top lip that are connected by the nose. Distal to the philtrum, bilateral clefts can be seen.
There are two types of cleft palate.
- Cleft palate (unilateral)
- Isolated Bilateral Cleft Palate- Isolated cleft palate is a solitary entity. It can affect the hard palate, the soft palate, or both.
Genetic and environmental factors are the most prevalent causes of cleft lip and palate. Folic acid, iron, and iodine deficit have all been linked to clefts. It can also happen as a result of stress.
Environmental factors during pregnancy include maternal smoking, cigarette usage, illicit drug use, and alcohol intake. Certain drugs, such as steroids or those recommended for seizures, cancer, arthritis, TB, and other conditions, can be addictive. Drug doses are being increased. Women who use oral contraceptives are often unaware that they are pregnant.
During the embryonic period of the foetus, exposure to some viruses or infectious illnesses such as measles. In industrial environments, exposure to hazardous chemicals, vapours, insecticides, gunpowder gases, nuclear radiation, X-rays, gamma rays, or poisonous reagents has dangerous consequences.
Consanguious marriage is the major cause of genetic incidence. TGF(8), TGF3(14,15) and transcription factors like MSX1, IRF6, and TBX22 are among the genes involved.
In the early stages of infancy, surgical repair of a cleft lip and palate is critical. It aids in the alleviation of feeding difficulties. At different periods of life, different surgical operations are done.
- At the age of three months, cleft lip surgery is required.
- At the age of 9-10 months, cleft palate surgery should be performed.
- Bone morphogenic protein (BMP) is used to treat alveolar cleft defects in children aged 3.5 to 4 years (Alloplast). If autograft is chosen, it can also be repaired around the age of 7.5 to 8 years.
- Pharyngoplasty is most commonly performed between the ages of 3-6 years.
